
The propensities of the amino acids calculated from a large non-redundant database of proteins are found to be highly position-specific and vary continuously throughout the length of the β-strand.
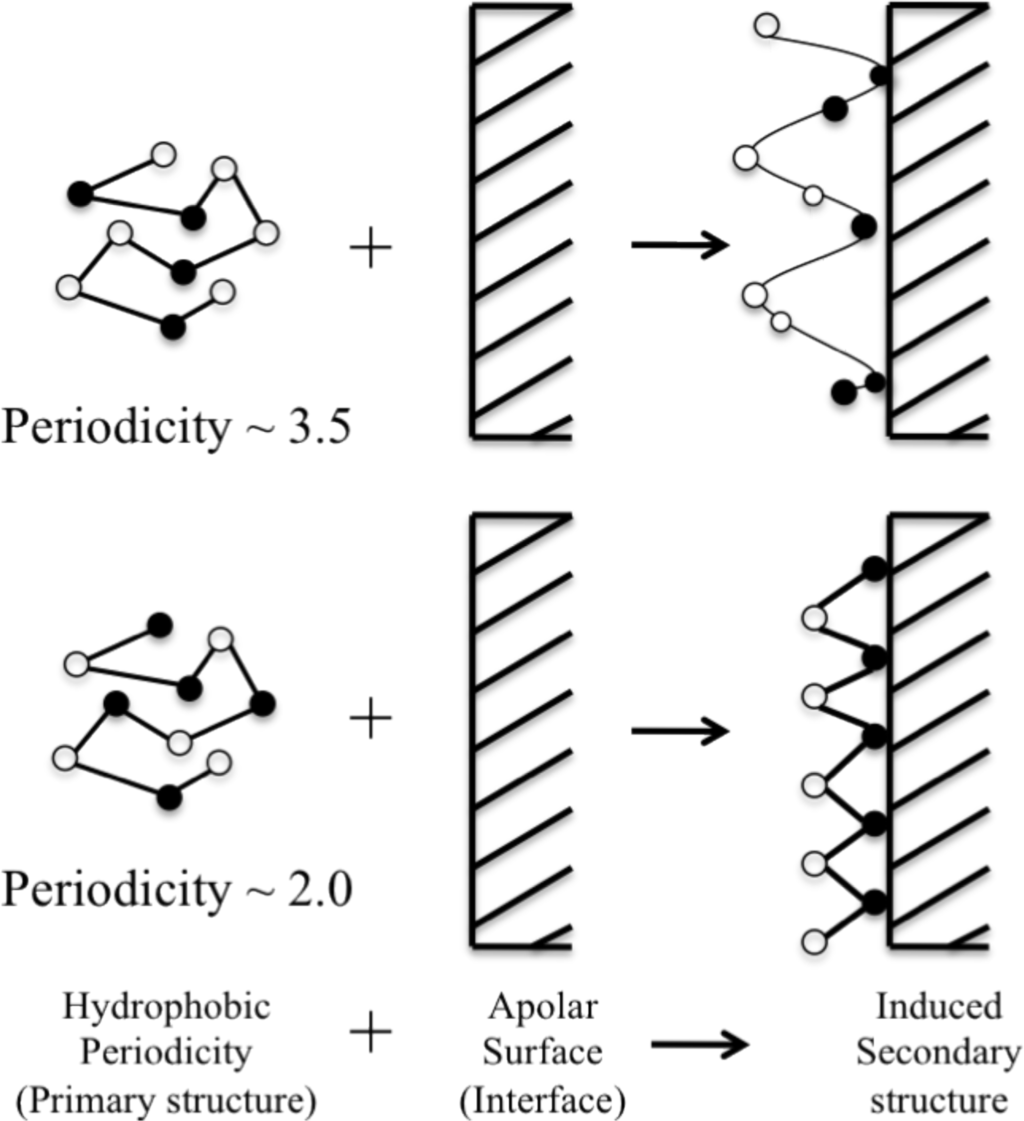
However, a comprehensive analysis of the sequence dependent amino acid propensities at positions between the ends of the β-strand has not been investigated.
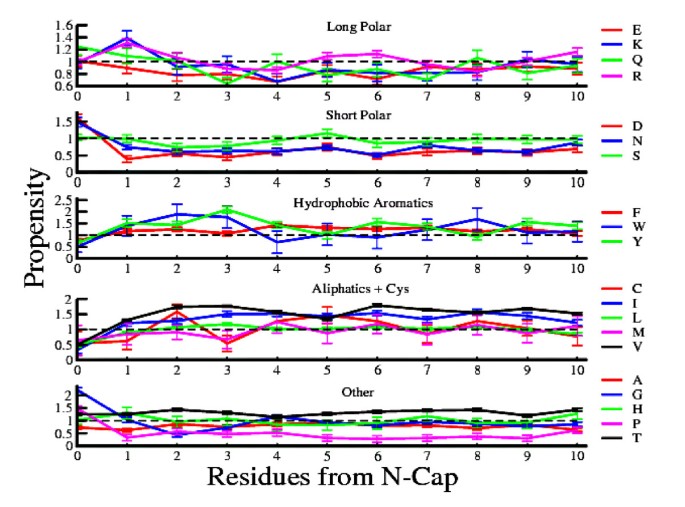
Recent studies have shown that most of the amino acids have significantly high or low propensity towards both ends of β-strands. Despite the importance of β-strands as main building blocks in proteins, the propensity of amino acid in β-strands is not well-understood as it has been more difficult to determine experimentally compared to α-helices.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
